| Schedule | Classes | Onsites | Manuals | Customers | Contact | About |
This page reviews the three different VBA module types; what type of procedures they contain; and how to view, control, and type in them.

Additional Tutorial Topics:
VBA code > is typed and viewed in the VBA Editor in what are called modules. A collection of modules along with other key elements is what is called a VBA project >.
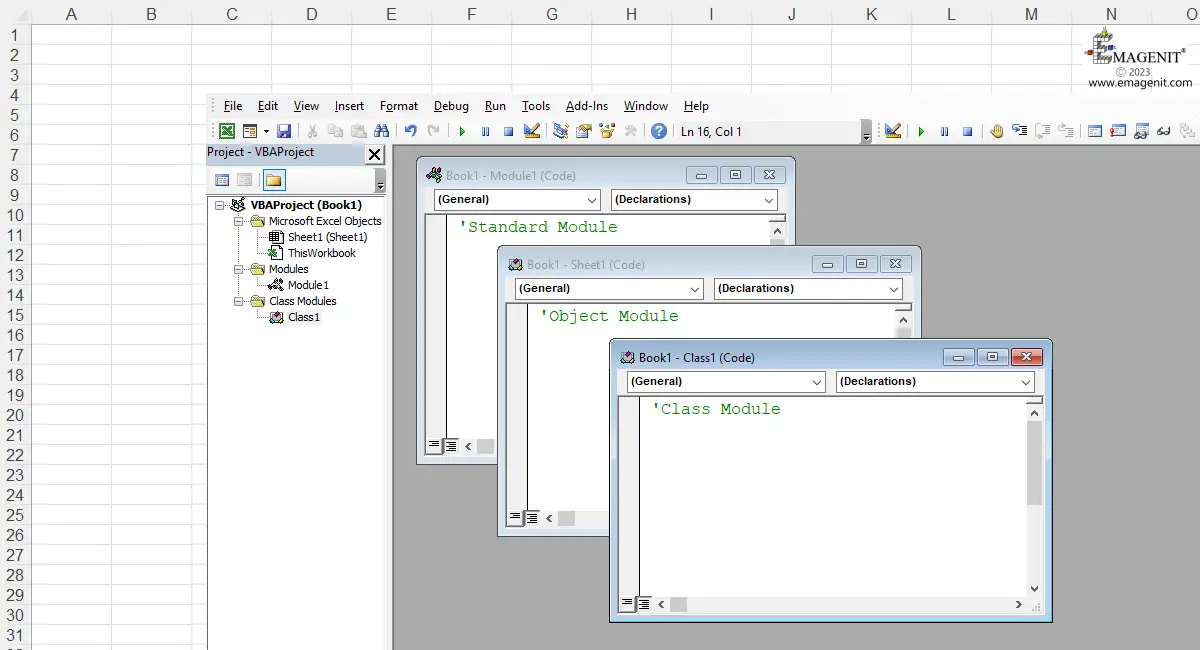
In the VBA Editor >, a VBA module resembles and behaves like a Word document when typing. When viewed, a VBA module will appear in its own window within the VBA Editor. Think of modules as organizational units for your code, you add VBA modules as needed to a project to organize and store your code. They come in three different types in VBA: Standard, Object, and Class modules.
A Standard module is where you will be typing most of your code when starting off in Excel VBA. Think of it as the town square, everybody can easily get to you and talk to you. You can assign shape and pictures to procedures in these modules to easily run them.
An Object module belongs to an Excel element like a workbook, chart, worksheet, or a VBA element like a userform. You create events in them (Sub procedures) that run when something occurs like pressing enter in a cell, opening a workbook, or clicking on a worksheet tab. These procedures can be used in place of clicking buttons to run code, but they require a lot of logic and programming know how to bring them under control.
A Class module is used to create a class for an object. Classes contain the code you use to command Excel, Word, PowerPoint..., but these are already made, you will just learn to run them. Object oriented programming involves advanced programming concepts so learn the fundamentals of programming first before you attempt to tackle them.
All of the modules just discussed appear in the Project Explorer window as icons. They are organized as follows: Standard modules are found under the Modules folder, Object modules are found under the Excel Objects folder, and Class modules are found under the Class Modules folder.
One note here, they all do look alike so you have to look at the name of the module and then locate it in the Project Explorer tree to tell what type it is.
Scroll < > picture if hidden.
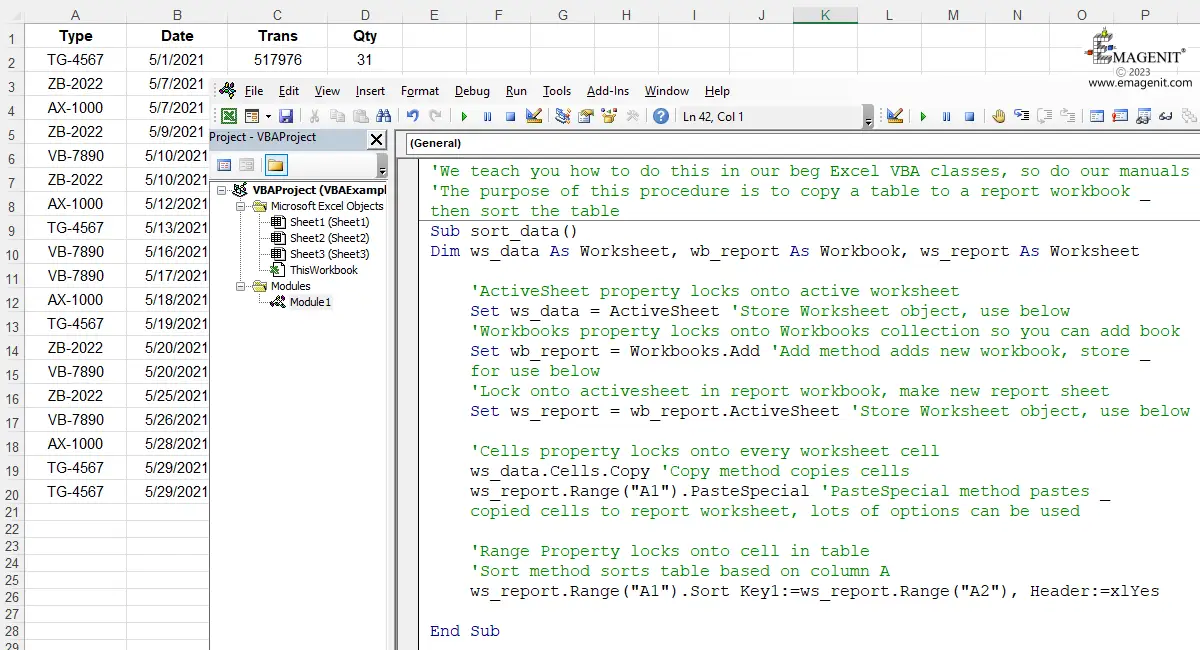
As stated earlier, modules are made up of elemental building blocks called procedures >. Procedures are used to organize and run your code in a module. Think of a paragraph in a Word document and you are on the right track.
You type Excel commands, variables, arrays, loops, logic, functions,... in your procedures and then run the procedure to control Microsoft Excel features and perform various tasks.
Scroll < > picture if hidden.
To view a module, just double click on its icon in the Project Explorer window. Standard modules are located under the Modules folder, Object modules are located under the Microsoft Excel Objects folder, and Class modules are located under the Classes folder. These folders can be viewed in the first image above.
Note that modules located under the Modules folder or Classes folder can be removed by right-mouse clicking on their icons in the Project Explorer window and selecting Remove. These two module types can also be added by proceeding to the Editor menu and selecting Insert / Module or Insert / Class Module.
Object modules can only be deleted by deleting the worksheet or chart sheet they are associated with. They are automatically added when you add a worksheet or chart sheet.
Scroll < > picture if hidden.
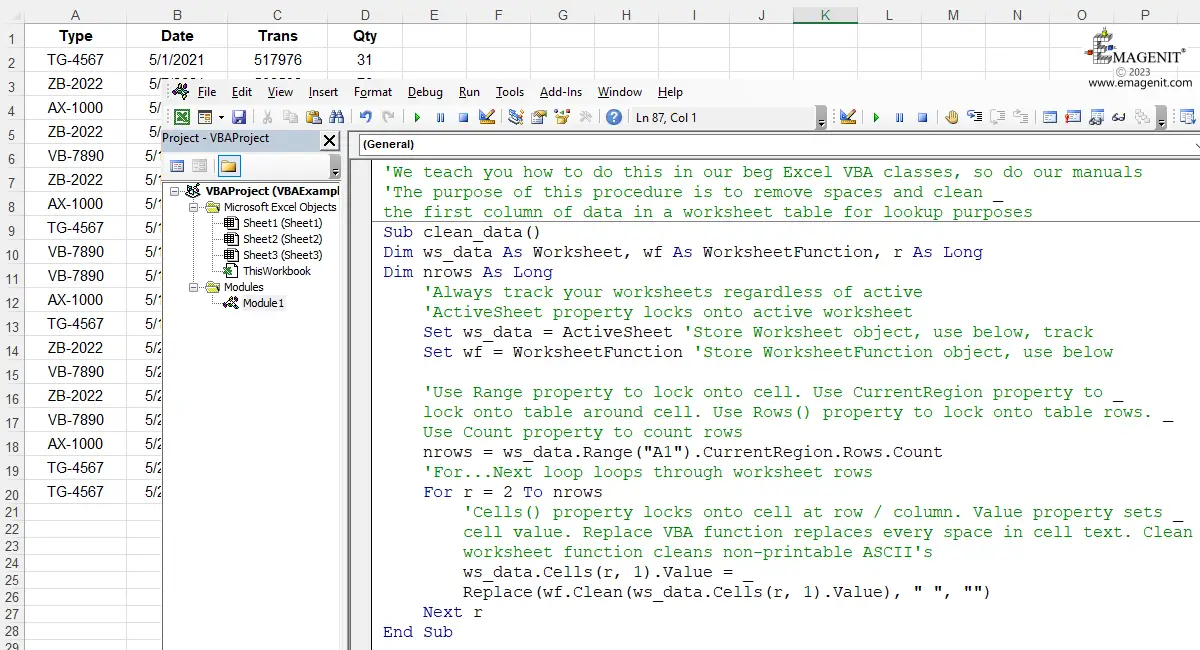
To type in a module, click in its window with your mouse and start typing VBA code. VBA does not start in any particular column or row and leaving blank lines in your code does not effect it.
You can use the Tab key to indent your code, you do this to make your code easier to read and interpret. To remove an indent in your code, just highlight the code and press Shift+Tab.
While typing in the module, you will notice 4 distinct text colors appear.
When typing Excel and VBA commands (i.e Functions, Properties, Methods...), a good test to see if you have misspelled what you are typing is to type everything in lower case then click off the line, if everything caps on the first letter, it is a least spelled correctly. This however does not indicate if it will run correctly.
A common mistake also encountered when correcting code is that you want to press Enter when done. Enter inserts a new line of code in the module and will split your statement (line of code) in two causing a compilation / syntax error. Just click off the line when you are done typing or go to the end of the line and press Enter.
When typing your computer code, most of your code is typed within a procedure's boundaries (Sub--->End Sub or Function--->End Function). Exceptions include Option statements, Declare statements, and Public / Private / Const / Type statements. These statements are typed at the very top of a module in the declaration section before any procedures are typed and only if they are needed.
Sub, Function, and Property procedures may all be typed in the same module, just make sure to name them uniquely. A procedure itself is limited to 64K in size, which means how much text is typed within its boundaries. It is a very large amount of code (~1000+ lines) and you will normally not bump up against it.
Scroll < > picture if hidden.
A common mistake is that VBA code must be stored in the same workbook as it is commanding. This is not true. You can store your VBA code in any workbook that you want. You will come to learn that the object expressions in your code (i.e. paths) are what allow you to control things in other workbooks, programs, databases...etc.
VBA code can search through Excel workbooks commanding what you tell it. You can lock onto workbooks using a variety of coding techniques, knowing the workbook name is not required. Keeping code in a single project workbook that is not attached to your data, models, charts, reports, and so forth prevents you from making 500 copies of your VBA code. This allows you to maintain version control for code upgrades.
A note here, when using VBA to create models in workbooks, it is recommended that you have only one model workbook. The idea is to build upload / download VBA code that controls model parameters and data. That way you can upgrade the model workbook and not have 100's of copies floating around. You can easily store model information in other workbooks or even text files. This strategy is great for batch processing and trade studies also.
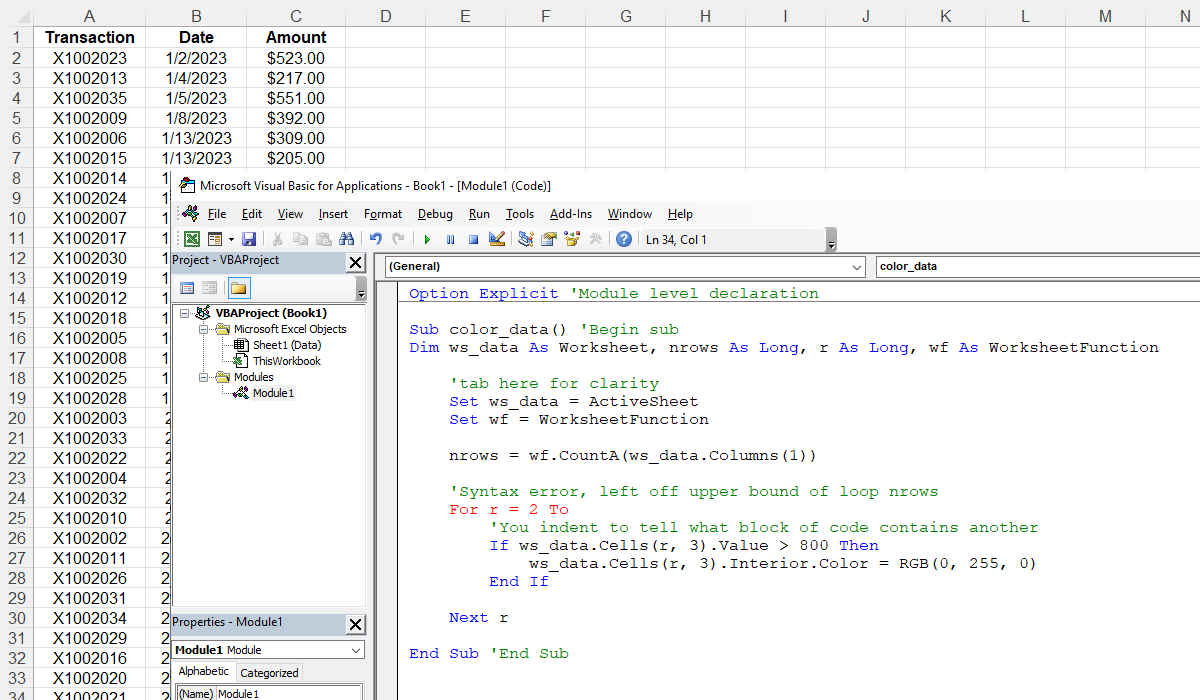
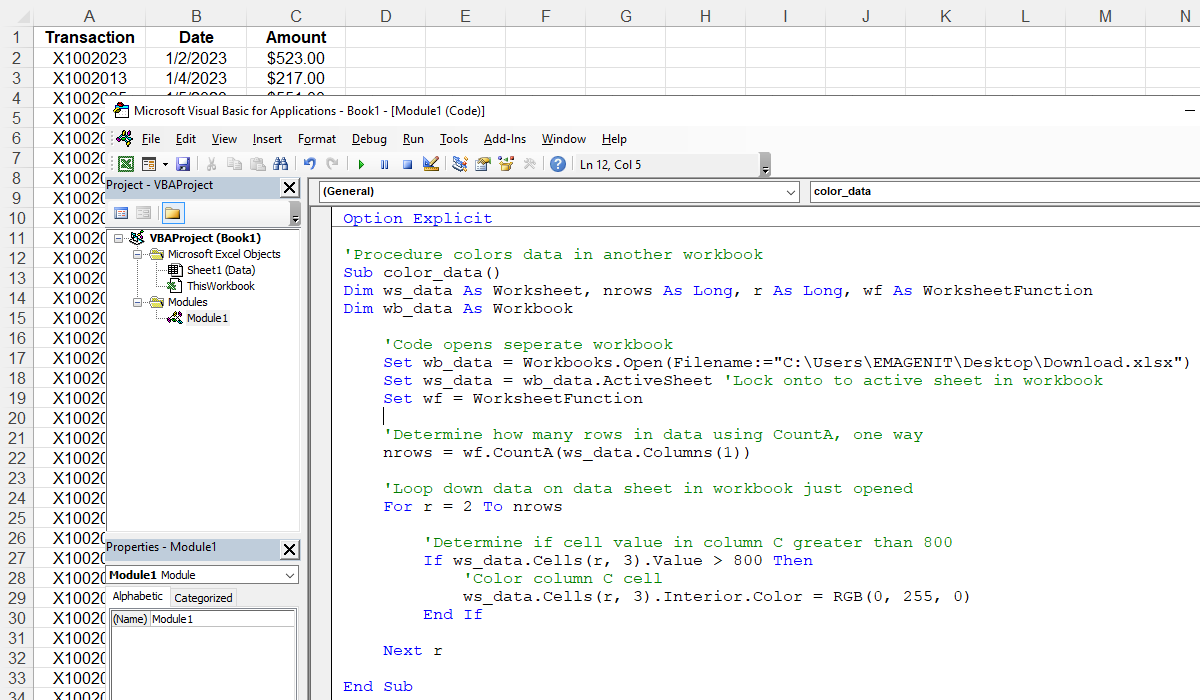
How VBA commands Excel is through object expressions (i.e. Command().Command().Command() ) commonly referred to as "paths". If you do not assume things are active in your VBA code and create the proper object expressions to track the Excel elements your are commanding, the code may be housed anywhere as stated eariler.
Relying on things being active is what causes most Excel VBA code to run slow and intermittently fail. While using the Macro Recorder is a very good research tool for figuring out specific Excel commands and their syntax, it writes horrible procedures. Learn to track objects in your code using object expressions that do not rely on anything being active and your code will be very robust in execution.
The Set statements you see in the code above are used to lock onto an active sheet initially, but then the variable ws_data is used in the object expressions commanding Excel after that point. You are tracking the sheet and that code will never fail because the sheet becomes inactive.
Scroll < > picture if hidden.
Excel Training Services
Excel Classes - Business and Industry
- Beginning Excel for Business and Industry
- Intermediate Excel for Business and Industry
- Advanced Excel for Business and Industry
- Excel Dashboards for Business and Industry
- Beginning Excel VBA for Business and Industry
Excel Classes - Engineers / Scientists
- Microsoft Excel for Engineers for Scientists
- Excel Data Analysis for Engineers and Scientists
- Excel VBA for Engineers and Scientists
- Excel VBA Data Analysis for Engineers and Scientists
Microsoft Excel Manuals
- Microsoft Excel Solutions Handbook
- Creating Advanced Excel VBA Apps
- Excel VBA Handbook for Engineers and Scientists
- Excel VBA App Design for Engineers and Scientists
EMAGENIT Company Information
US Military
Copyright © 2025
EMAGENIT All Rights Reserved